Products
Your catalog is composed of Products and ProductVariants.
A Product always has at least one ProductVariant. You can think of the product as a "container" which includes a name, description, and images that apply to all of
its variants.
Here's a visual example, in which we have a "Hoodie" product which is available in 3 sizes. Therefore, we have 3 variants of that product:
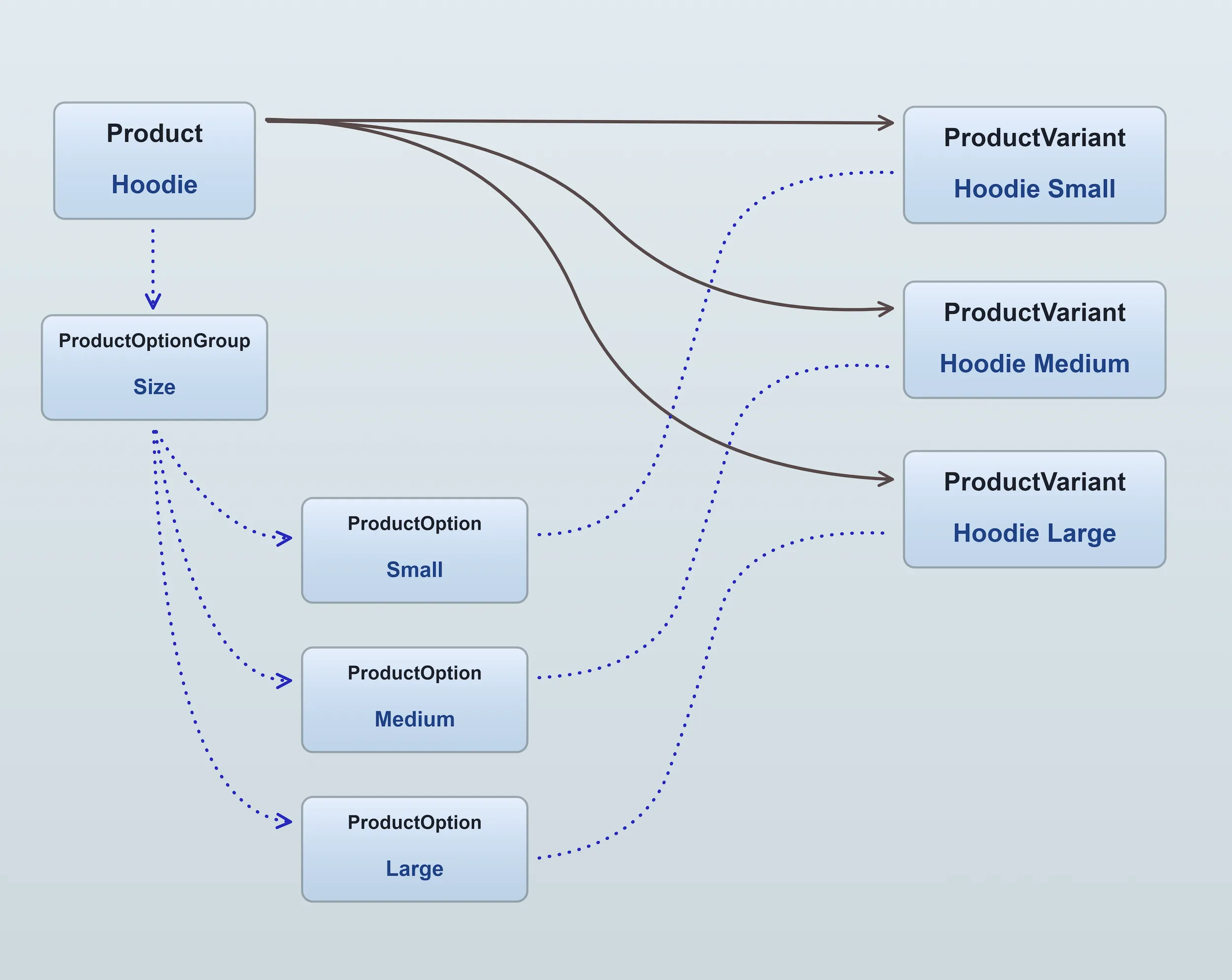
Multiple variants are made possible by adding one or more ProductOptionGroups to
the product. These option groups then define the available ProductOptions
If we were to add a new option group to the example above for "Color", with 2 options, "Black" and "White", then in total we would be able to define up to 6 variants:
- Hoodie Small Black
- Hoodie Small White
- Hoodie Medium Black
- Hoodie Medium White
- Hoodie Large Black
- Hoodie Large White
When a customer adds a product to their cart, they are adding a specific ProductVariant to their cart, not the Product itself.
It is the ProductVariant that contains the SKU ("stock keeping unit", or product code) and price information.
Product price and stock
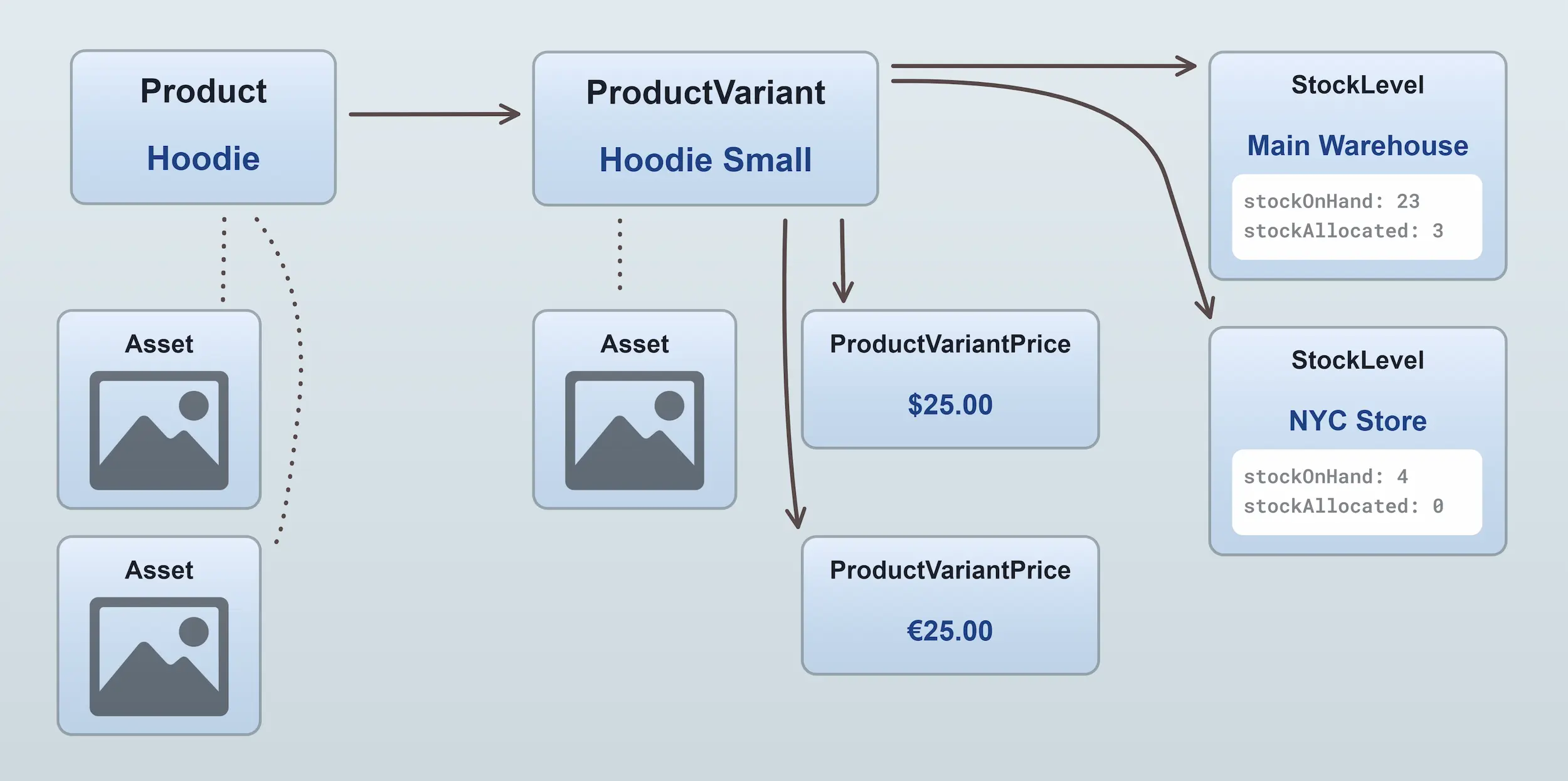
The ProductVariant entity contains the price and stock information for a product. Since a given product variant can have more
than one price, and more than one stock level (in the case of multiple warehouses), the ProductVariant entity contains
relations to one or more ProductVariantPrice entities and
one or more StockLevel entities.
Facets
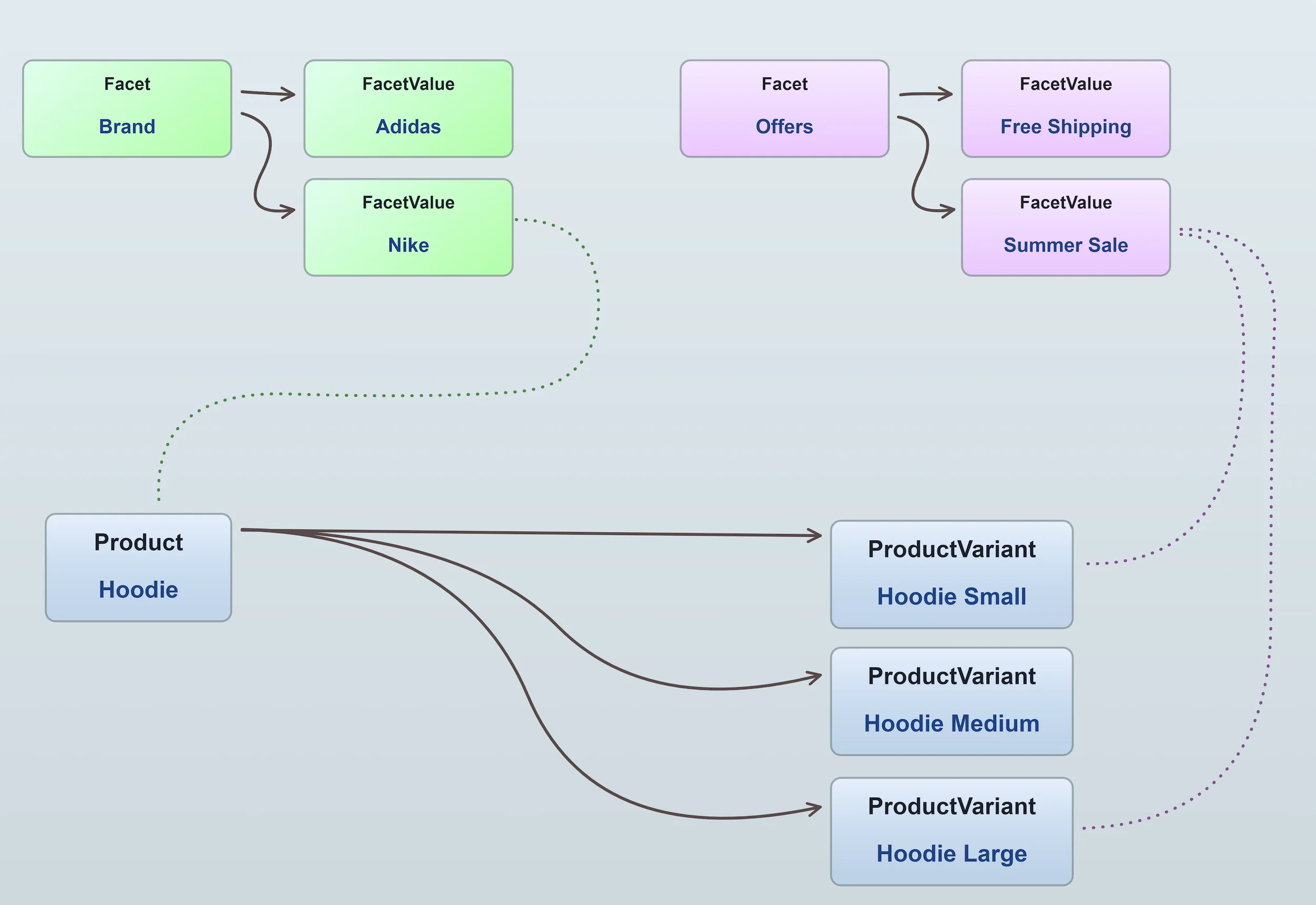
Facets are used to add structured labels to products and variants. A facet has
one or more FacetValues. Facet values can be assigned to products or
product variants.
For example, a "Brand" facet could be used to label products with the brand name, with each facet value representing a different brand. You can also use facets to add other metadata to products and variants such as "New", "Sale", "Featured", etc.
These are the typical uses of facets in Vendure:
- As the basis of Collections, in order to categorize your catalog.
- To filter products in the storefront, also known as "faceted search". For example, a customer is on the "hoodies" collection page and wants to filter to only show Nike hoodies.
- For internal logic, such as a promotion that applies to all variants with the "Summer Sale" facet value, or a shipping calculation that applies a surcharge to all products with the "Fragile" facet value. Such facets can be set to be private so that they are not exposed to the storefront.